Software Testing
Our Quality Engineering & Testing portfolio provides a full spectrum of software quality validation and testing services and our process works with you to assure you meet your business outcomes.
To do this we utilize our state-of-the-art Quality Engineering Delivery Centres, Digital Assurance Factories and Mobile Testing Centres of Excellence, both onshore, nearshore and offshore.
With our leading quality expertise, proven methodologies and accelerators, we assure increased customer value and measurable business outcomes from both your digital transformation programs and traditional core IT systems.
Our Business Goal
To be the trusted partner for organizations seeking excellence in leadership, operational efficiency, and transformative growth.
Fast, codeless, and reliable testing that helps you ship features with confidence
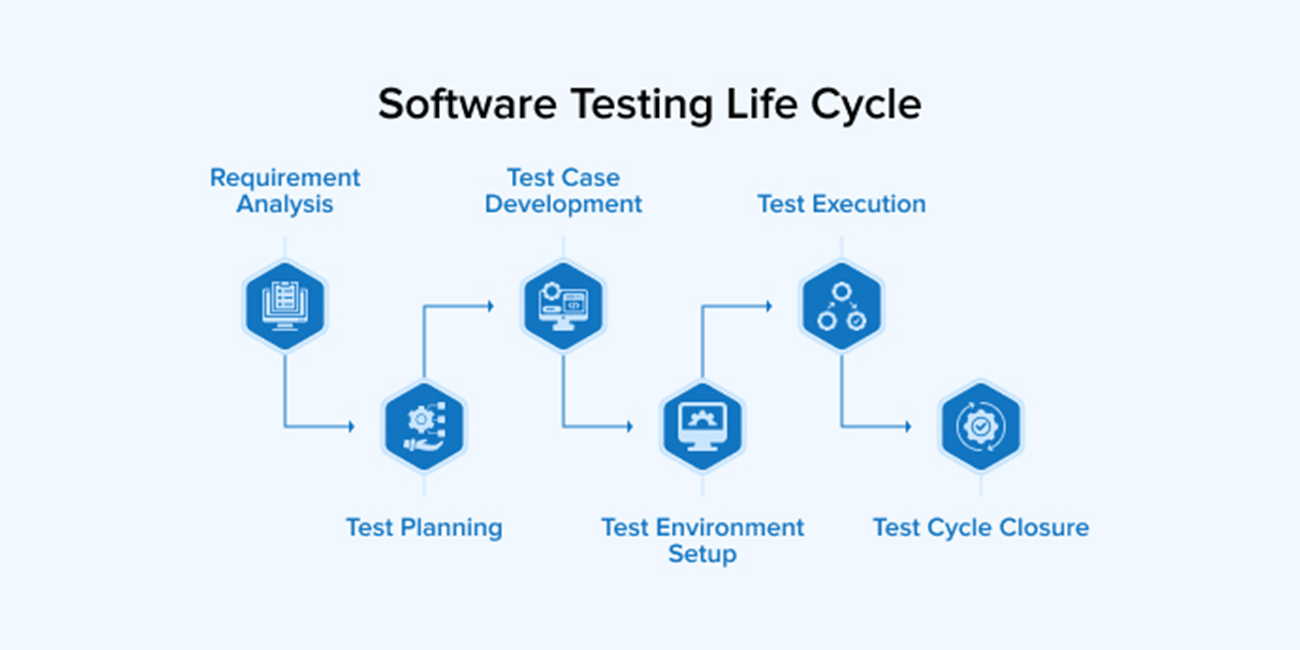
Software testing is the process of evaluating and verifying that a software application or system functions as intended. It involves executing software components to find bugs, errors, or other issues before the software is released or deployed. Here’s an overview of the key aspects of software testing
Manual Testing : Involves manually checking software for defects without using automated tools. Testers execute test cases by hand and compare actual outcomes with expected results.
Automated Testing : Uses tools and scripts to automate the execution of tests, which can save time, especially for repetitive or high-volume testing tasks.
White Box Testing : Tests internal structures or workings of an application, typically done by developers who have knowledge of the code.
Integration Testing : Verifies that multiple components or systems work together as expected. Examines the complete system to ensure it meets the specified requirements.
Functional Testing : Focuses on ensuring that the software performs its intended functions. Evaluates aspects such as performance, usability, reliability, and scalability.
Technologies we use for developing
Manual Testing : Involves manually checking software for defects without using automated tools. Testers execute test cases by hand and compare actual outcomes with expected results.
Automated Testing : Uses tools and scripts to automate the execution of tests, which can save time, especially for repetitive or high-volume testing tasks.
White Box Testing : Tests internal structures or workings of an application, typically done by developers who have knowledge of the code.
Integration Testing : Verifies that multiple components or systems work together as expected. Examines the complete system to ensure it meets the specified requirements.
Functional Testing : Focuses on ensuring that the software performs its intended functions. Evaluates aspects such as performance, usability, reliability, and scalability.